Check out our White Paper Series!
A complete library of helpful advice and survival guides for every aspect of system monitoring and control.
1-800-693-0351
Have a specific question? Ask our team of expert engineers and get a specific answer!
Sign up for the next DPS Factory Training!

Whether you're new to our equipment or you've used it for years, DPS factory training is the best way to get more from your monitoring.
Reserve Your Seat TodayMIB, SNMP, and OID are all features that help facilitate your network monitoring and communication smoothly.
Understanding what each one means, and how it operates will help you understand how to set up yourself (as a network administrator) or your employees (as someone in charge of a network administrator).
You want to ensure that your network monitoring equipment is supplied by a manufacturer that doesn't attempt planned obsolescence or vendor lock-in.
A MIB (Management Information Base) is a crucial part of SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol). It is a structured collection of information about managed devices in your network.
MIBs are defined by using a hierarchy of names that are then identified using OID (Object Identifier).
MIBs use a language named SMI (SNMP MIB Definition Language) to define the syntax and structure when creating MIB modules in your SNMP framework.

In the Management Information Base (MIB), you can encounter two primary types of objects: scalar objects and tabular objects.
Scalar Objects: These are used to represent a single instance of an object. Think of them as individual data points providing specific information.
Tabular Objects: These represent multiple instances that are interconnected, often organized within MIB tables. This structure allows for the management and monitoring of complex systems by grouping related data.
Understanding these objects is crucial for efficient network management, as they define how information is systematically organized and accessed within a MIB.
SNMP offers further abilities if there is a Trap Receiver Rule Engine being utilized. The Rule Engine within a Trap Receiver allows for advanced processing and filtering of these incoming traps. It works by defining rules or criteria to handle the traps effectively, which might include:
Finding manufacturers that offer SNMP, especially SNMPv3 (The latest and most secure version of SNMP) means that you won't be limited by vendor lock-in.
OIDs (Object Identifiers) are alphanumeric strings (containing both letters and numbers) that serve as unique identifiers for objects in a MIB.
OIDs map out the structure of the MIB in a tree format. Each OID represents a specific managed object. Where each object is on the tree is relevant to its relationship with other objects.
Managed objects in a MIB are organized hierarchically. Each level reflects different aspects or categories of the object.
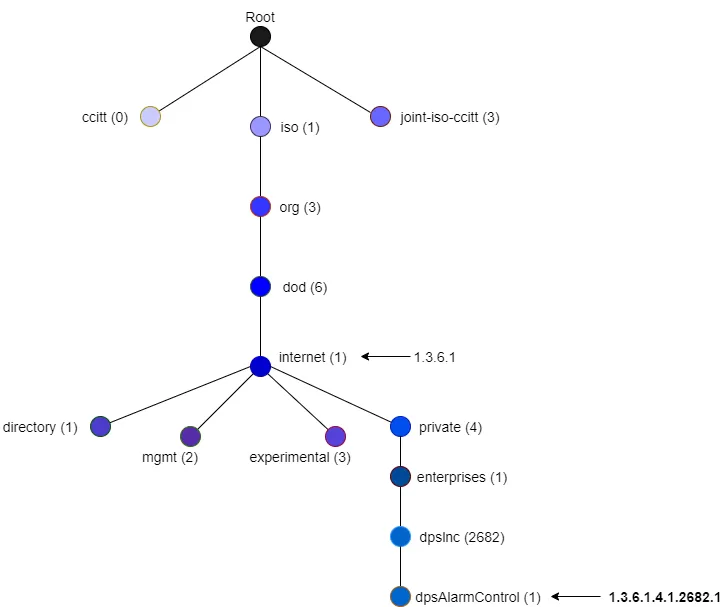
OIDs are assigned so that no two objects share the same alphanumeric string in the MIB.
Top-level OIDs are the highest-level identifiers within a MIB. They are the root nodes in your MIB tree and are typically reserved for standard organizations.
Administrators can use OIDs to efficiently navigate and access information stored in the MIB.
OIDs can additionally help you manage the features of different vendor equipment in the following way:
1.Understand Your Device's Capabilities: Check the device documentation or vendor-provided MIB files. These files list all the OIDs the device supports, organized into a readable tree structure.
2.Download the Relevant MIBs: Use software like T/Mon or third-party SNMP tools to parse the MIBs. These tools translate OIDs into human-readable formats and let you browse through available data points.
3.Query the Device: Use SNMP walk commands to explore the device's supported OIDs interactively. This method works well when the documentation isn't complete or you want to see real-time data.
By systematically navigating through the MIBs and testing OIDs, you'll identify the exact data points you need for effective monitoring. Always ensure compatibility with your SNMP manager, such as T/Mon, to streamline integration.
MIBs are hierarchical databases that describe the structure of data on a device, like temperature readings, system uptime, or fan status. OIDs are the unique addresses that point to specific pieces of information within that hierarchy. In practical terms, the MIB is the roadmap, and the OID is the specific destination.
SNMP has evolved over the years and has had multiple versions released. First, let's look at the key differences and features between each SNMP version:
It introduces a level of security and privacy for SNMP traffic by offering three key capabilities:
These security enhancements make SNMPv3 the preferred choice for securely managing network devices.
It is specifically designed to meet the requirements for a secure environment, thus making it indispensable for modern network management strategies.
Transitioning to SNMPv3 from older versions provides a significant uplift in network security posture, ensuring that sensitive information and control capabilities are well protected.
DPS Telecom has multiple resources to help bring you up to speed on SNMP, MIB, and OID. We make telecom monitoring equipment and have experts who can train you and provide resources to help you.
If you're looking for more quick information, we have numerous whitepapers on specific network monitoring topics (click here)
If you have an urgent problem without proper vendor support to bring you back online quickly, please feel free to contact me and I will do my best to help you.
Although vendor lock-in and planned obsolescence are common among manufacturers that are trying to make quick money. Others recognize that reliability sells.
Finding a manufacturer that can work with your other equipment can be difficult. I can help guide you in the right direction.
Call at 800-693-0351 -or- Email sales@dpstele.com

Ziad Alezabi
Ziad Alezabi is a Application Documentarian at DPS Telecom. He reviews successful DPS client projects and reports on the best practices that you can use to successfully reach your own project goals.