Finding and solving problems in your SNMP implementation can be tough.
This guide helps you identify and solve SNMP issues.
1-800-693-0351
Have a specific question? Ask our team of expert engineers and get a specific answer!
Sign up for the next DPS Factory Training!

Whether you're new to our equipment or you've used it for years, DPS factory training is the best way to get more from your monitoring.
Reserve Your Seat TodayFirst of all, keep in mind that a firewall is a network security device that works to monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic and makes decisions in terms of allowing or blocking determined traffic based on a set of security rules.
Firewalls are essential tools in safeguarding various network endpoints, from personal computers to large-scale enterprise data centers. By implementing strong security controls, they act as a critical first line of defense against a wide range of cyberattacks.
Key Benefits of FirewallsDetection and Prevention: Firewalls help detect suspicious activities and prevent intrusive attacks early in their lifecycle.
Traffic Regulation: By regulating incoming and outgoing traffic, firewalls help organizations enforce zero-trust security policies, ensuring that only legitimate data flows through the network.
Compliance: They also play a vital role in helping businesses stay compliant with security and data protection standards, reducing the risk of costly breaches or penalties.
Understanding these capabilities can aid in troubleshooting firewall issues, ensuring that your network remains secure and resilient against evolving threats.
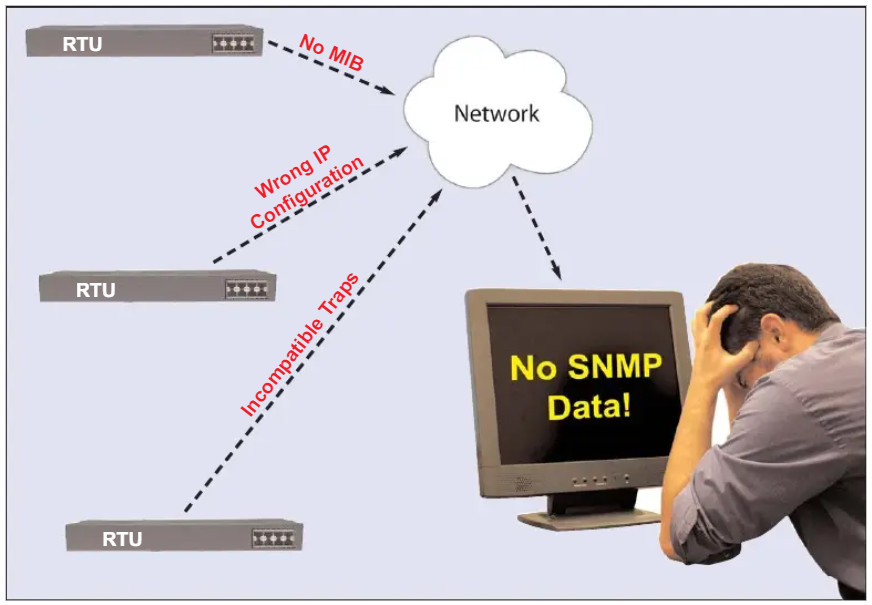
Firewall problems usually result from three main conditions:
Keeping these conditions in check is essential for a secure, well-functioning network. Proper firewall configuration and access can make all the difference in ensuring your network runs smoothly and safely.
Some SNMP problems are not directly caused by either manager or agent. The network connectivity between the two devices can sometimes be impeded by firewall settings. Firewalls that block UDP, SNMP, pings, or ports 161 or 162 are the most common issues. Certain companies also have their own specific firewall errors.
Beyond these, several other misconfigurations might expose your network to vulnerabilities:
Addressing these common issues can enhance your firewall's effectiveness and strengthen your overall network security.
Use the following steps to identify and solve firewall errors:
Ping a PC near the device
A simple ICMP ping to a PC near the device is a good initial test to determine connectivity status and network performance issues. ICMP ping is an IP-based signal sent from one device to another. If the target device receives the "ping" from the source device, it will (if configured to do so) respond to confirm that it is active and connected to the network. It's a simple way of confirming that a device is online.
So, if your pings to the PC are not returned, try pinging the gateway. Continue working your way up the network with your pings to identify the point where they stop. Check for firewalls and firewall configurations, especially those that block UDP, SNMP, pings, or ports 161 or 162. Keep in mind that some networks block all ping traffic as a security measure.
Ping the device
Next, send another simple ICMP ping to the device to determine connectivity.
If pings to the PC in Step 1 were successful, but pings sent to the device fail, the problem is almost certainly with your SNMP device.
Telnet and/or browse to the device
If the SNMP device you are testing supports Telnet connections or Web access, you should attempt to connect using one of these methods. If pings succeed but Telnet and/or browsing is blocked, this is a very good indication that you have a firewall issue.
Determine the traffic flow
Once connectivity tests point toward a firewall issue, it's crucial to determine the flow of traffic. Assess whether the issue arises when traffic is directed to or through the firewall. This distinction helps narrow down the possible causes. Perform the following checks:
Review any recent updates that might have altered firewall settings, and consider rolling back if necessary. Scrutinize firewall permissions and logs for any error messages or warnings that could indicate where traffic is being blocked. Examine firewall rules and configurations, adjusting them to ensure they allow intended traffic flow.
Routine maintenance troubleshooting
Create a checklist based on your specific firewall setup to conduct routine maintenance. This proactive approach helps identify potential issues before they disrupt traffic flow. Monitor the network consistently, testing as needed, until you confirm that the problem is resolved.
Trace the route to the device
Tracing the "hops" that network traffic follows to reach the device can allow you to pinpoint a tricky firewall issue. A simple trace can be performed from the Command Prompt of Windows XP:
Open a Command Prompt in Windows XP
Type "tracert", a single space, and the IP address of the device you are trying to reach (i.e. "tracert 192.168.230.143")
Press return to start the trace
Show the output to your IT department to identify potential firewall problems
By following these comprehensive steps, you can systematically identify and resolve common firewall-related connectivity issues, ensuring a smoother network operation.
All DPS Telecom products include comprehensive technical support. If you've purchased one of our products and are encountering any kind of issue, contact DPS Tech Support today at 559-454-1600.
At DPS Telecom, the representative who answers your call isn't an intern reading from a script. DPS Tech Support representatives are engineers who contribute to product development. And, if your problem requires additional expertise, the DPS Engineering Department that designed your product is right down the hall.
Help us connect you to the right engineer by filling out this quick questionnaire. Simply leave your contact information to get started, and we'll call you back. Most preliminary discussions are about 15 minutes, and afterward, we'll send you a custom application diagram of a recommended solution that'll make it easier to justify your project to management.