Check out our White Paper Series!
A complete library of helpful advice and survival guides for every aspect of system monitoring and control.
1-800-693-0351
Have a specific question? Ask our team of expert engineers and get a specific answer!
Sign up for the next DPS Factory Training!

Whether you're new to our equipment or you've used it for years, DPS factory training is the best way to get more from your monitoring.
Reserve Your Seat TodayDistributed Antenna Systems (DAS) have become the backbone of modern wireless coverage - especially in large campuses, high-rise buildings, and critical facilities like hospitals. However, efficiently monitoring these systems can be a challenge.
Using SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) can help make this process easier. SNMP provides a standardized method for retrieving, filtering, and managing network device data - which is perfect for multi-vendor DAS environments.
This includes ADRF DAS solutions, which one of my clients recently asked me about monitoring with an SNMP manager. That's because ADRF DAS devices can send real-time alerts (SNMP traps) whenever certain performance thresholds are crossed.
In this guide, you'll discover how to use SNMP commands - alongside multiple master stations - to successfully monitor DAS parameters.
Whether you're new to SNMP or just looking to optimize your existing DAS monitoring, my goal is for these tips to help you maintain network reliability and proactively resolve issues.

This is a topology diagram for 16 tower sites. They all have LAN connection. This allows RTUs in NEMA enclosures to communicate back to your SNMP manager. The RTUs can also send email/SMS directly to smartphones.
SNMP enables efficient, real-time DAS monitoring because it's:
You can use SNMP commands - such as SNMP GET, SNMP WALK, and SNMP SET - to gather actionable DAS metrics.
Using SNMP for DAS monitoring enhances the reliability of the system, offering:
By using these SNMP-based capabilities to your advantage, you're saving valuable time and resources.
Getting started with SNMP on your ADRF DAS devices typically involves:
Once SNMP is enabled, you can confirm communication with a simple SNMP WALK command from your SNMP command-line interface, which often looks something like this example from the commonly used Net-SNMP software:
snmpwalk -v2c -c public 192.168.X.X .1.3.6.1.4.1Remember:
public with your SNMP community string and 192.168.X.X with the DAS device's IP.Here are some common commands to gather DAS data while testing and troubleshooting your system. They serve as a precursor to setting up your SNMP manager for recurring monitoring on an interval:
SNMP GETs retrieve a single OID value. For example:
snmpget -v2c -c public 192.168.X.X .1.3.6.1.4.1.XXXXX.1.2.0This might return the current signal strength or temperature reading.
SNMP WALK commands iterate through a range of OIDs for a comprehensive overview. For example:
snmpwalk -v2c -c public 192.168.X.X .1.3.6.1.4.1.XXXXXThis is great for discovering which metrics your ADRF DAS device supports.
SNMP SETs modify a device parameter (e.g., setting a threshold or toggling a system value). For example:
snmpset -v2c -c private 192.168.X.X .1.3.6.1.4.1.XXXXX.1.5.0 i 1The private that appears in this command is typically the write community string. The i 1 at the end of the command indicates an integer value of 1.
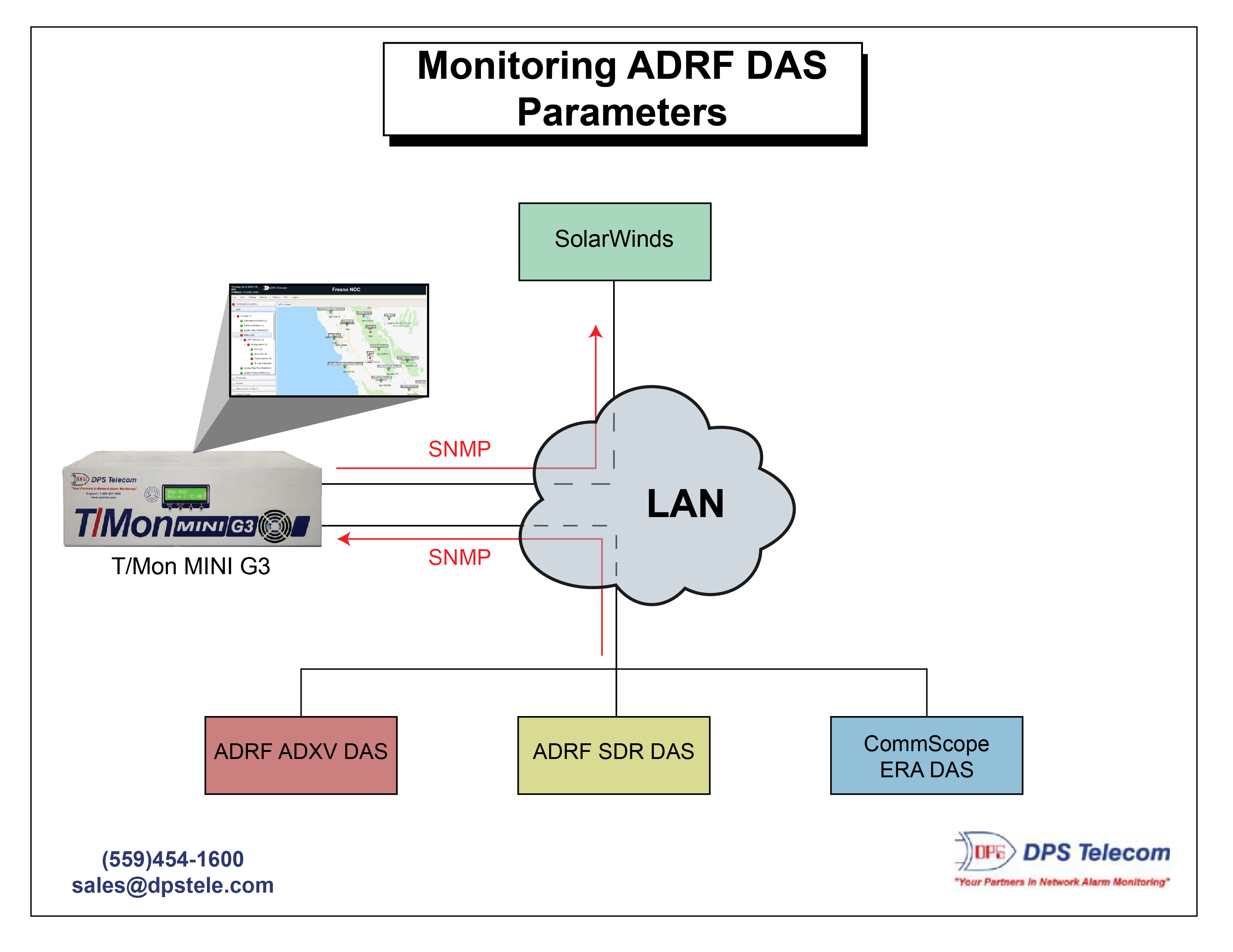
Even with strong SNMP capabilities, DAS failures can happen. Some of the most common issues include power supply failures, signal degradation, and overheating. While these issues can cause unexpected failures, using a SNMP manager like the T/Mon MINI G3 can help you stay ahead and prevent these failures in the future.
Whether you're managing a single building or an entire campus, T/Mon MINI G3 offers:
Alarm Collection in T/Mon involves the master receiving and filtering SNMP traps from other network devices. You can correlate related alerts (e.g., power + temperature) to pinpoint root causes.
SNMP commands don't have to be solely between T/Mon and DAS components. You can forward alerts to a second master station like SolarWinds for further alarm monitoring capabilities.
Configuring T/Mon to forward essential SNMP alerts to your SolarWinds (or any other brand's) SNMP manager helps unify your monitoring. This second master station can display DAS alerts within your broader network dashboard, so you don't miss anything. You can also use this function to effectively convert non-SNMP alarms into SNMP that an SNMP manager can actually use.
This integration reduces response times, eliminates tool-hopping, and helps organize your entire network into a cohesive system.
Suppose a major hospital relies on an ADRF DAS for consistent cellular coverage in operating rooms and emergency wards. They face frequent false alarms and lack strong escalation.
Using T/Mon as a monitoring solution provides:
This solution results in a more reliable DAS environment. The system ensures continuous mobile connectivity for critical hospital communications.
To deploy this master station into your existing system:
Knowing how to use Net-SNMP commands like SNMP WALK, SNMP GET, and SNMP SET is only half the battle. Real success comes when you combine these SNMP tools with a centralized alarm management platform like T/Mon MINI G3. You'll not only gather raw data - you'll convert it into actionable insights, prioritize alerts, and scale your operations across multiple sites.
Contact DPS for help developing a strong SNMP monitoring solution for your DAS. Our monitoring experts will guide you through a custom solution that meets your unique requirements.
Don't let DAS issues catch you off-guard. We'll help you design a strong, proactive monitoring strategy now.

Andrew Erickson
Andrew Erickson is an Application Engineer at DPS Telecom, a manufacturer of semi-custom remote alarm monitoring systems based in Fresno, California. Andrew brings more than 19 years of experience building site monitoring solutions, developing intuitive user interfaces and documentation, and opt...