Check out our White Paper Series!
A complete library of helpful advice and survival guides for every aspect of system monitoring and control.
1-800-693-0351
Have a specific question? Ask our team of expert engineers and get a specific answer!
Sign up for the next DPS Factory Training!

Whether you're new to our equipment or you've used it for years, DPS factory training is the best way to get more from your monitoring.
Reserve Your Seat TodayICS (Industrial Control Systems) security aims to safeguard industrial processes and control networks.
Every network element has to have data protection to keep people out of where they shouldn't be. With increased automation of your systems, the impacts of these attacks on your elements could impact core system operations.
People and technology must work together to develop processes that can fight intentional - or accidental - security threats. So, let's take a look at some facts about ICS network security, its top six weaknesses, and what you can do to avoid them at your company.
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) is one of the most common types of ICS. SCADA networks are responsible for providing automated control and remote human management of essential services, such as water, natural gas, electricity, and transportation to millions of people.

SCADA security involves the protection used for SCADA networks. SCADA systems need to be protected because, just like any other network, they are under threat from cyber-attacks that could bring them down quickly.
In 2016, the US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), conduct 130 assessments in FY 2016. The following image shows us their results.
Let's dive into the six most commons security breaches in the ICS environment and how you can handle them to protect your system.
Network experts are growing concerned that fundamental network equipment might be vulnerable to Internet-based attacks. New best-practice standards recommend that network equipment should be secured from open Internet access.
NERC (North American Electric Reliability Council) is developing a new reliability standard called Cyber Security Standard CIP-002-1. This new standard recommends several security procedures for computer-controlled systems, including restriction of unnecessary network services, securing dial-up modem connections, anti-virus software, and formal policies for managing user access and passwords.
SCADA systems are capable of providing you with a wide variety of functions. Some of these functions, normally provided by default, may not be necessary for your monitoring needs. Extraneous features, such as 3rd-party modules or "bells & whistles" potentially compromise your network without any added value.
When you have unused or unnecessary features, it increases the danger of unauthorized connection on your devices, unauthorized transfer of information, and unauthorized tunneling.
Review the functions and features provided by your SCADA system to determine which capabilities are candidates for removal.
Securing your SCADA & ICS systems from unauthorized users can be difficult.
So, you need an RTU platform that includes SNMPv3 (remember that SNMP is a communications protocol) encryption as a standard feature.
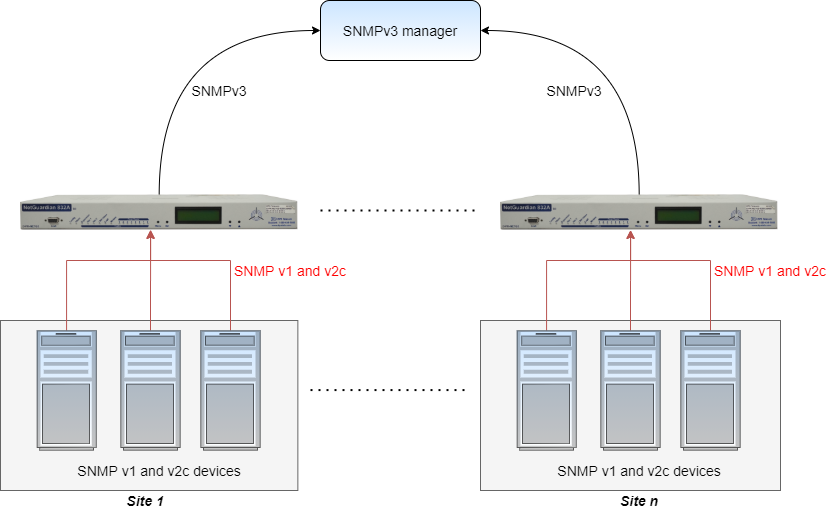
Here are the 2 types of security available in SNMPv3:
Authentication
Authentication is used to ensure that traps are read by only the intended recipient.
Privacy
Privacy encrypts the payload of the SNMP message to ensure that it can't be read by unauthorized users. Any intercepted traps will be filled with garbled characters and will be unreadable.
Security of critical infrastructure is an especially important consideration. Regulating and controlling personnel access is vital to protecting and maintaining expensive gear. Increased site security acts as an obstacle to vandalism and theft due to your ability to monitor facility access.
This added security can give you peace of mind that only authorized personnel access your facilities.

You need a comprehensive building management system that integrates into an existing alarm management platform. With this system in place, a log of all site access, including the time of day and location that access was granted, is maintained.
Sometimes it's impossible to find security breaches without gluing yourself to your screen 24x7. Unless, of course, your RTU box supports analog trending and graphing.
Trending is a massive help for multiple reasons - it ultimately makes the invisible become painfully obvious.
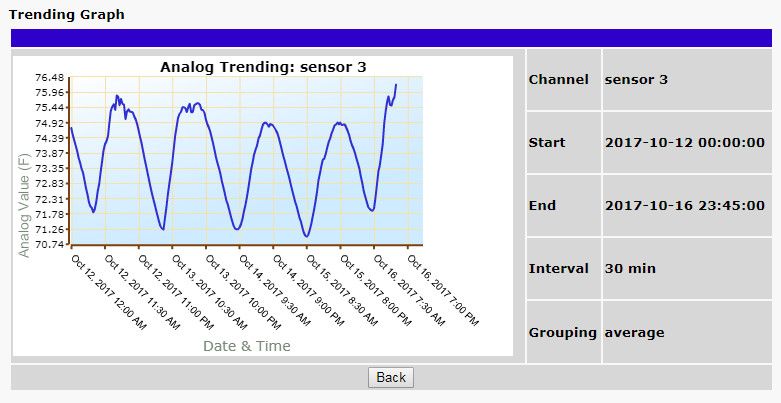
Some monitoring devices have analog trending capabilities built into their web interface. If you have this feature, then you're ahead of the game. The next step is utilizing it to understand your analogs and overall network health.
Looking at raw analog trend data is a good first step, but it's still easy to miss something.
Using graphs to visually represent analog data can make trends and potential problems stand out like a sore thumb.
Without the ability for a technician to access the database of alarms and activities, or for the administrator to edit permissions and usage restrictions, you may as well be attempting to fly blind. While allowing wide-open access from across the network is out of the question, many people have tried to implement various security measures to verify the user attempting to gain access.
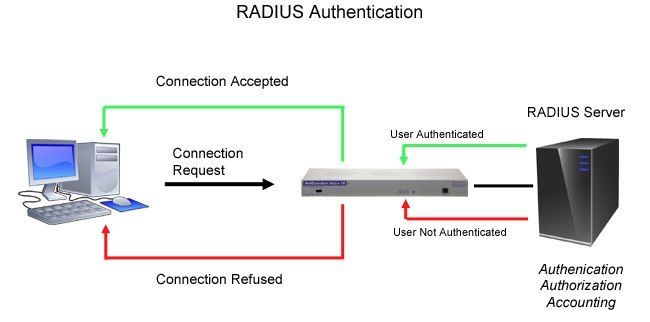
RADIUS - Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service - is a way to manage logins to many different types of equipment in one central location. Using the client/server format, RADIUS passes user information to designated servers and acts on the response that is returned.
Every time a device receives a login attempt (usually a username and password), it requests authentication from the central RADIUS server. If the username and password combination is found in the server's database, an affirmative "access granted" reply is sent back to the device, allowing the user to connect.
It's vital that you take some time to review your general security practices surrounding the remote monitoring of your automation and control system.
If you're looking for a secure RTU, consider the NetGuardian 832A with SNMPv3 support to send encrypted traps to your master so unintended recipients can't simply look at the messages.
If you're looking for a secure master station, our T/Mon also has the option to support HTTPS web viewing, and - like the NetGuardian line - it has passwords that control the level of access individual users have to the system.
Give us a call - we can help you start enhancing your ICS security today.

Morgana Siggins
Morgana Siggins is a marketing writer, content creator, and documentation specialist at DPS Telecom. She has created over 200 blog articles and videos sharing her years of experience in the remote monitoring industry.