Download our free SCADA tutorial.
An introduction to SCADA from your own perspective.
1-800-693-0351
Have a specific question? Ask our team of expert engineers and get a specific answer!
Sign up for the next DPS Factory Training!

Whether you're new to our equipment or you've used it for years, DPS factory training is the best way to get more from your monitoring.
Reserve Your Seat TodaySupervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) is a system that aims to monitor and control field devices at your remote sites. SCADA systems are invaluable in industries where real-time monitoring and data acquisition are crucial. These systems are critical as they help maintain efficiency by collecting and processing real-time data.
(This information is a small section of our full SCADA Tutorial PDF download.)
A SCADA system is a combination of hardware and software that enables industrial process automation by capturing Operational Technology (OT) real-time data. It connects sensors that monitor equipment like motors, pumps, and valves to an onsite or remote server, ensuring seamless communication and control.

With SCADA, organizations can achieve:
Control: Manage processes locally or remotely.
Data Acquisition: Gather, analyze, and display real-time data.
Interaction: Directly engage with industrial equipment such as sensors, valves, pumps, and motors.
Event Recording: Document and archive events for reporting and future reference.
Depending on the configuration, the state of industrial processes can be viewed from an operator workstation in the plant, a Human-Machine Interface (HMI) beside machinery, or even from an employee's home. This flexibility underscores the adaptability of SCADA systems to various operational needs.
The main goal of this supervisory system is to monitor and control equipment in the industrial processes for companies in the public and private sectors. As technology advances, SCADA systems continue to integrate with modern protocols and IoT devices. As a matter of fact, in today's world, there are SCADA systems almost everywhere. This includes industrial plants, manufacturing, transportation, oil and gas, power distribution, water control and etc.
For example, SCADA systems are commonly used within the renewable energy sector. These systems remotely monitor and control installations, collect and analyze data, detect faults, and optimize energy output. Among diverse sectors, SCADA systems provide a framework for smooth operations and regulatory compliance. Across the board, SCADA systems enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
Let's dive deeper into SCADA functions and the components that make SCADA operations possible.
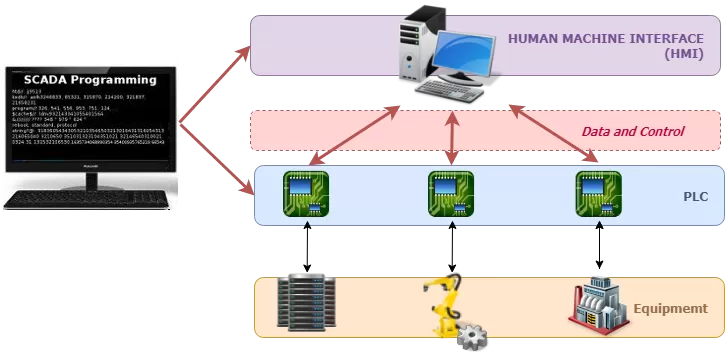
SCADA Diagram Example System with Main Components
SCADA systems perform several functions that allow for proper management of remote facilities. The following are the core functions of a SCADA system.
Included in their functions and abilities, SCADA systems are able to ensure compatibility among varying equipment from different vendors. The flexibility of a SCADA system makes it essential for managing diverse equipment landscapes. These SCADA systems allow for data compatibility by supporting a wide range of communication protocols. Supporting multiple protocols is necessary for this compatibility as various manufacturers use different protocols for data exchange.
SCADA systems achieve this compatibility through protocol conversion. This conversion enables the system to translate data from one protocol to another, maintaining smooth communication between devices. Additionally, many SCADA systems are built to support industry-standard protocols such as Modbus, DNP3, or SNMP, which are widely adopted by equipment vendors. This allows SCADA systems to gather and manage data from multiple sources, regardless of the equipment manufacturer. This creates a smooth integration and interoperability across the SCADA network.
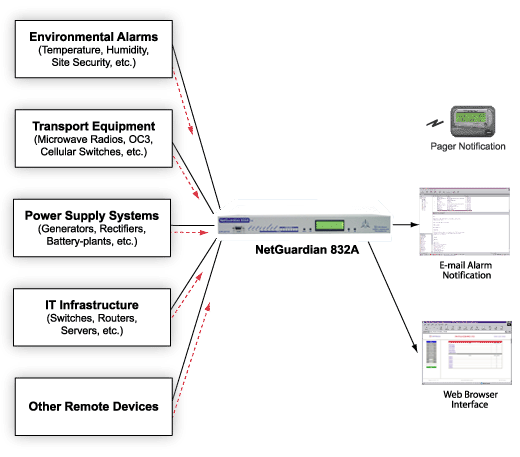
In addition to protocol conversion, SCADA systems handle alarms and events. Alarms and events in SCADA systems are critical components that uphold the smooth and safe operation of industrial sites. These systems handle alarms and events by continuously monitoring the data from connected devices and triggering alerts when predefined conditions are met. When a parameter - such as temperature, pressure, or voltage - exceeds its normal range, the SCADA system generates an alarm. These alarms can be displayed on the system's interface, sent via email, or even communicated through text messages. These alarms are prioritized based on severity, allowing operators to respond to critical issues quickly.
SCADA systems also log events, capturing time-stamped records of all alarms and changes in the system's state. This logging feature is another reason SCADA systems are indispensable in maintaining operational oversight. SCADA systems use these event logs to keep track of equipment health and help with predicting when machinery might fail. This reduces unplanned downtimes and protects your entire SCADA network.
Through logging events, operators are able to review system performance, track incidents, and analyze historical data to prevent future issues. By examining event logs and historical data, you can find trends and gain insights into past performance. Strong SCADA systems can also automate responses - such as shutting down equipment or rerouting power - to minimize damage before operators intervene. This automation further solidifies the role of SCADA systems in maintaining efficient operations.
If you plan to deploy a SCADA system, then you need to know and understand the four important system components that present in every SCADA network. Yours might be tailored to your specific requirements, but it will need the following basic components.
Having a SCADA system in place is critical to help maintain efficiency, process network data for informed decisions, and to address problems before they affect network uptime.
However, designing and implementing a SCADA network or telemetry system that can handle the needs of your unique network sometimes isn't that simple. It's common to overspend on software and hardware that you'll never use - this might result in wasted opportunities to improve your network efficiency and wasted budget.
You probably can't stop all your daily tasks to focus only on your SCADA deployment. So it can be difficult to learn all the details that make an efficient SCADA system.
If that's your case, then we have the solution for you. Our Fast Introduction to SCADA Fundamentals and Implementation white paper is a quick, 12-page introduction to SCADA. This guide shows how you can use SCADA effectively and profitably. Concrete applications and examples are included as illustrations and to reinforce best practices.
Start planning your perfect-fit SCADA solution. Download your free PDF copy of the Fast Introduction to SCADA Fundamentals and Implementation.
Next Page: DPS Telecom Remote Site Survey
All DPS Telecom products include comprehensive technical support. If you've purchased one of our products and are encountering any kind of issue, contact DPS Tech Support today at 559-454-1600.
At DPS Telecom, the representative who answers your call isn't an intern reading from a script. DPS Tech Support representatives are engineers who contribute to product development. And, if your problem requires additional expertise, the DPS Engineering Department that designed your product is right down the hall.
Help us connect you to the right engineer by filling out this quick questionnaire. Simply leave your contact information to get started, and we'll call you back. Most preliminary discussions are about 15 minutes, and afterward, we'll send you a custom application diagram of a recommended solution that'll make it easier to justify your project to management.