Check out our White Paper Series!
A complete library of helpful advice and survival guides for every aspect of system monitoring and control.
1-800-693-0351
Have a specific question? Ask our team of expert engineers and get a specific answer!
Sign up for the next DPS Factory Training!

Whether you're new to our equipment or you've used it for years, DPS factory training is the best way to get more from your monitoring.
Reserve Your Seat TodayWhen managing any network, it's crucial to have strong monitoring solutions in place. Integrating a reliable monitoring system for your Modbus generators is the only way to make sure your remote sites have a consistent power supply.
This technology isn't just a choice. A reliable remote monitoring system is a must for preventing network downtime and failures. A robust monitoring system will also boost performance, guarantee reliability, and allow you to tackle issues before they become major problems.

Modbus is a widely-used communication protocol used in industrial automation systems. It's a protocol that exchanges data between different devices and control systems.
Modbus protocol uses a master-slave architecture. The master sends a request command to one or more slave devices, and the slave device responds with the requested data.
One of the core concepts of Modbus is the Modbus register. This is an addressable storage location in a device. Through these registers, you can monitor important stats like temperature, pressure, and flow rate.
It is important to have an effective system in place to monitor your Modbus generator. A reliable monitoring solution can automatically generate Modbus data traffic to test or simulate the system.
Overall, Modbus protocol is a reliable and flexible means of communication that is critical to various industrial processes.
Here's a breakdown of the key components of Modbus protocol:
With a better understanding of components and their roles, your Modbus devices will be more efficient and reliable.
These components work together to ensure that devices can communicate with each other effectively. Understanding the various components of Modbus and how they function is essential for anyone working with automation devices. This way, you can make sure your devices are working as they should and are communicating well with other devices on your network.
There are a few things you must do to provide constant power to your facility. If your system includes all these elements, you'll ensure optimal performance and prevent potential issues. Implementing these best practices will also ensure the longevity and effectiveness of your generator.
In this video, you'll see a few simple steps on how to monitor your generator using Modbus. We'll start polling data from a backup generator (propane/diesel). This example uses the web interface of the NetGuardian DIN remote monitoring device.
You can implement all these elements of generator maintenance with monitoring technology, namely an RTU (remote telemetry unit).
A robust generator monitoring system relies on a Remote Telemetry Unit (RTU) to ensure a steady power supply. The RTU acts as the eyes and ears, providing real-time data on the generator's status and performance from a distance.
An RTU can gather, store, and share data over networks. This is crucial for monitoring key parameters like power output, fuel levels, engine performance, and environmental conditions.
By using an RTU, operators can quickly spot issues, reduce downtime, and prevent damage or outages. The RTU can also connect with other systems for predictive analytics and alarms. This boosts the power supply's reliability and efficiency.
Including an RTU in your setup supports uninterrupted power supply operation. It also helps the generator to consistently power facilities.
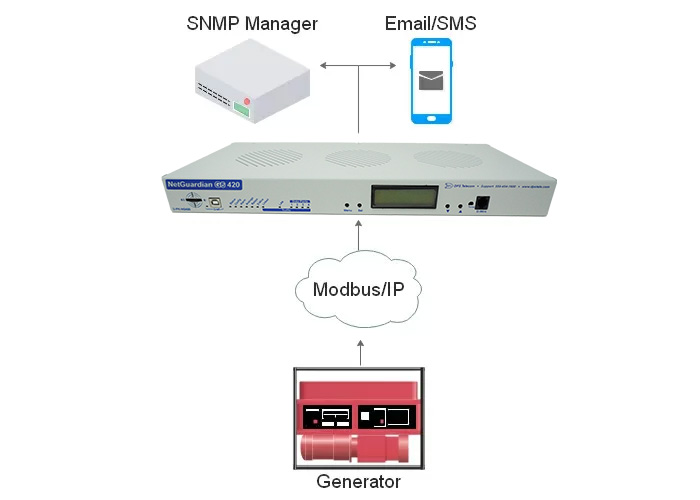
By following best practices and implementing a suitable setup, operators like you can ensure optimal performance and prevent downtime. Modbus generator management is necessary to ensure a reliable and efficient power supply. By following these guidelines, you can ensure the longevity and effectiveness of your generator. So don't wait any longer - start implementing these best practices today for a more reliable tomorrow!
DPS Telecom provides monitoring solutions for several of the top ten power corporations in the US.
One of these large companies contacted us needing a way to monitor Modbus generators. Their network includes a large number of fiber cabinets with generators. One of this major power company's goals was to be able to quickly disconnect parts of their grid.
This fiber cabinet monitoring project began with a series of phone calls with our sales team. We prepared a detailed proposal explaining how they could deploy the NetGuardian DIN at their remote sites. Our in-depth technical proposals include diagrams and specifications for each device.
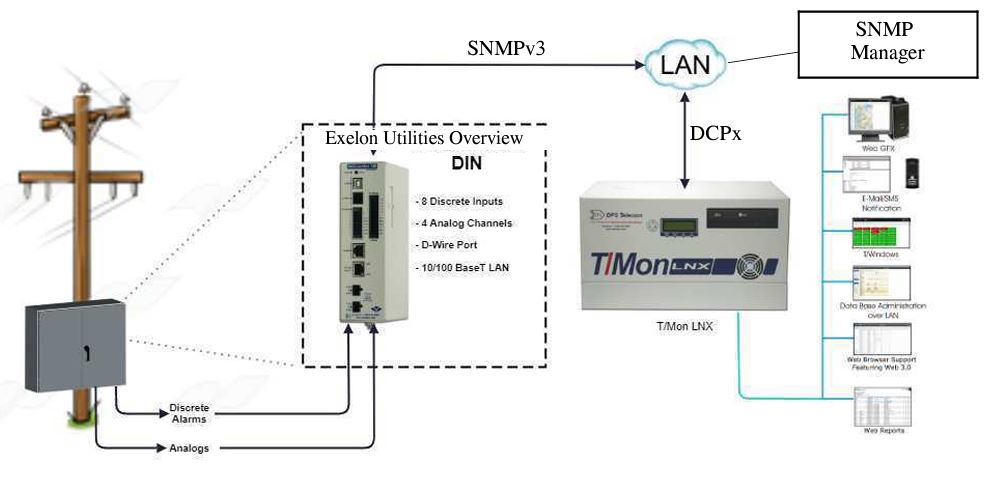
The proposed system diagram shows a series of interconnected NetGuardian DIN units distributed across the client's power grid. Each unit monitors critical points, such as generators and substations.
The T/Mon central monitoring station receives real-time insights and alerts from these units via Modbus protocol. The solution also includes redundancy features. Even if a unit fails, the client could still monitor their remote sites.
This smart configuration enhances reliability and efficiency in monitoring the vast grid infrastructure, embodying a perfect-fit solution tailored to the client's specific needs.
For this project, the power company deployed around 40 NetGuardian DINs across their infrastructure to monitor their Modbus generators. This solution offered a huge benefit to the power company.
Now they have instant access to run time, exercise time, LPG tank levels, and more. This information allows their staff to schedule preventative maintenance better and react quickly to any potential problems.
Are you in need of a generator monitoring solution that fits your specific needs? DPS Telecom's expert team will work with you to design a solution that meets your exact requirements. We have almost 4 decades in the remote monitoring industry!
Every facility is different and requires a tailored approach. Don't settle for a one-size-fits-all solution, trust DPS Telecom for your generator monitoring needs.
We can help you make sense of complex topics like Modbus registers. We can also give you insight into how to keep your generator working at peak performance!
Don't waste any more time searching for answers online when you can get personalized support from the leaders in the industry. Give DPS Telecom a call at 800-693-0351!

Haley Zeigler
Haley is a Technical Marketing Writer at DPS Telecom. She works closely alongside the Sales and Marketing teams, as well as DPS engineers, resulting in a broad understanding of DPS products, clients, and the network monitoring industry.