Check out our White Paper Series!
A complete library of helpful advice and survival guides for every aspect of system monitoring and control.
1-800-693-0351
Have a specific question? Ask our team of expert engineers and get a specific answer!
Sign up for the next DPS Factory Training!

Whether you're new to our equipment or you've used it for years, DPS factory training is the best way to get more from your monitoring.
Reserve Your Seat TodayMany organizations and companies that provide services depend on LAN/WAN networking equipment, but there's a long list of issues that may arise from one of those network devices. Some of these issues include loss of revenue, customer dissatisfaction, and decreased productivity.
Whenever a device fails, the first line of action is to cycle power or reboot. But, this can be challenging if the gear is not easily accessed or is located in a remote location. It's not practical, and most of the time, it's very costly to send techs out to remote sites every time equipment needs to be rebooted.
A remote power controller is designed to solve these kinds of problems so downtime can be reduced. It will immediately cycle power or reboot a piece of equipment without interrupting other devices. It also allows you to troubleshoot problems - from any location in the world. But, for that, you need to make sure your controller is efficient and reliable.
In this article, we'll go through the most important features you need to keep in mind when choosing your remote power controller.

The operation of a remote power controller is actually quite simple. At your data center or equipment site, you'll install a small rack-mounted electronic box that has several power outputs on its back panel. Then, you'll plug your equipment (servers, switches, etc.) into those outputs.
With a power input and many outputs, it can look a lot like a rack-mounted power strip. The big functional difference is the remote management of each power output port. Through a remote connection (usually LAN), you can command a remote power controller to turn on, turn off, or reboot any single piece of connected equipment.
Remote power control devices can be used in many different settings, and that's because they bring numerous advantages. Some of these advantages are:
There are many options of remote power controllers in the market, so you must know what you should look for. Having an efficient power controller is important to maximize your investment and productivity.
So, here's a list of features the best remote power controllers have:
In an IT or office setting, you generally operate on AC power, so you need an AC power controller.
In industrial telecom environments, you'll usually be running on DC power (-48VDC is the most common). These scenarios demand a DC-capable remote power controller.
The fuses or circuit breakers on a power controller are an important protection against equipment overload and damage. Some controllers, however, have a poor design that makes accessing fuses and circuit breakers difficult.
Make sure to look for a power controller that puts them in a prominent location where they won't be blocked by cabling or other obstacles.
Every power controller has some finite amperage (current flow) that it can handle. You need to make sure that the power controller you choose has adequate capacity to support the devices that will be connected to it.
Keep in mind that there are typically two thresholds to consider.
First, each output port will have a maximum current. Each device that you connect to the power controller must have a power consumption at or below this level.
Second, the controller itself can have a total current capacity. The total power draw of all connected devices must be at or below this level as well. Don't forget that the total current capacity may be less than the sum of each output's capacity. For example, a remote power controller might support 10 amps on each of its 8 power outputs, but only support a total of 50 amps.
When you and your team visit a site, sometimes you'll need to manipulate power directly.
That's why it's a good idea to choose a remote power controller with front-panel buttons or switches to toggle power. Imagine how silly you'll feel cracking open a laptop to access the remote interface for a device that's 2 feet in front of you.
Another helpful feature for on-site control is a "remote lockout" function. This allows an on-site tech to disable remote power switching temporarily. This helps to eliminate confusion when both on-site and remote users are trying to troubleshoot a problem.
The on-site technician is given exclusive control since that person will presumably be in a better position to troubleshoot. This also helps to reduce safety risks associated with unexpected energizing of electrical wiring.
If you have more than a few mission-critical telecom devices or servers, you know that many of them have dual-redundant power supplies. This is an important feature to protect your service's reliability, but it can create hassles when you're actually trying to power down or reboot a device.
Smart power controllers have paired output ports, enabling you to toggle redundantly powered devices with one command. Keep in mind, however, that any power controller that supports paired outputs should also have dual inputs. Otherwise, you're forced to run both of your device's power supplies from the same power source, reducing your resistance to power failures.
Most of the time, techs need not only remotely control power but also monitor their mission-critical devices as well. Many remote power management solutions also allow you to do just that.
Here are some remote alarm monitoring options that your power controller can be equipped with:
All remote power controllers have some sort of remote interface. Some interfaces are just better than others.
The first big difference you can look for is the platform. A lot of controllers have a software application you need to install on your workstation. This can cause trouble when you're suddenly using a different PC. Now you have to track down a copy of the software and install it again.
It's far better to choose a remote power controller with a built-in web interface. That way, any workstation with a web browser is capable of remotely accessing your power controller. You'll just type the device's IP address into your browser's address bar.
For security against unauthorized intrusions, the web interface should at least be password-protected. At some security-conscious organizations, it's also important to have a web interface that's secured via HTTPS (SSL) encryption.
To know how much power each of your devices is monitoring, current draw monitoring on each power controller output port is ideal. This way, you can view (ideally through the web interface) how much electricity is flowing through each port.
As an alternative, you can reduce your costs by monitoring the total current passing through the power controller instead of on a per-port basis. This requires that your manufacturer only includes a single current sensor, rather than one for every controller output port.
If you're going to connect a dozen or more pieces of key equipment to a power controller, shouldn't it be the most reliable equipment you have? After all, if it fails, your connected devices will lose power.
That's why you need to choose a remote power controller with a proven history of reliability in real environments just like yours. Ask prospective vendors about their existing customer base. You can also look for positive indicators of reliability like a durable metal chassis and in-house product testing (for example, EMI and stress testing).
If your remote power controller doesn't have upgradeable firmware, it will never get any better after your purchase. Firmware upgrades allow you to take advantage of the latest manufacturer-created improvements and fixes. Sometimes, entirely new features will boost your remote management efficiency.
If you're wondering how you will find a device that attends all the previous points, then you don't have to worry. Our DC Remote Power Switch (also available in AC power version) is an efficient remote power controller that allows you to operate controls, check the temperature at your sites, and monitor power consumption - all from your office PC.
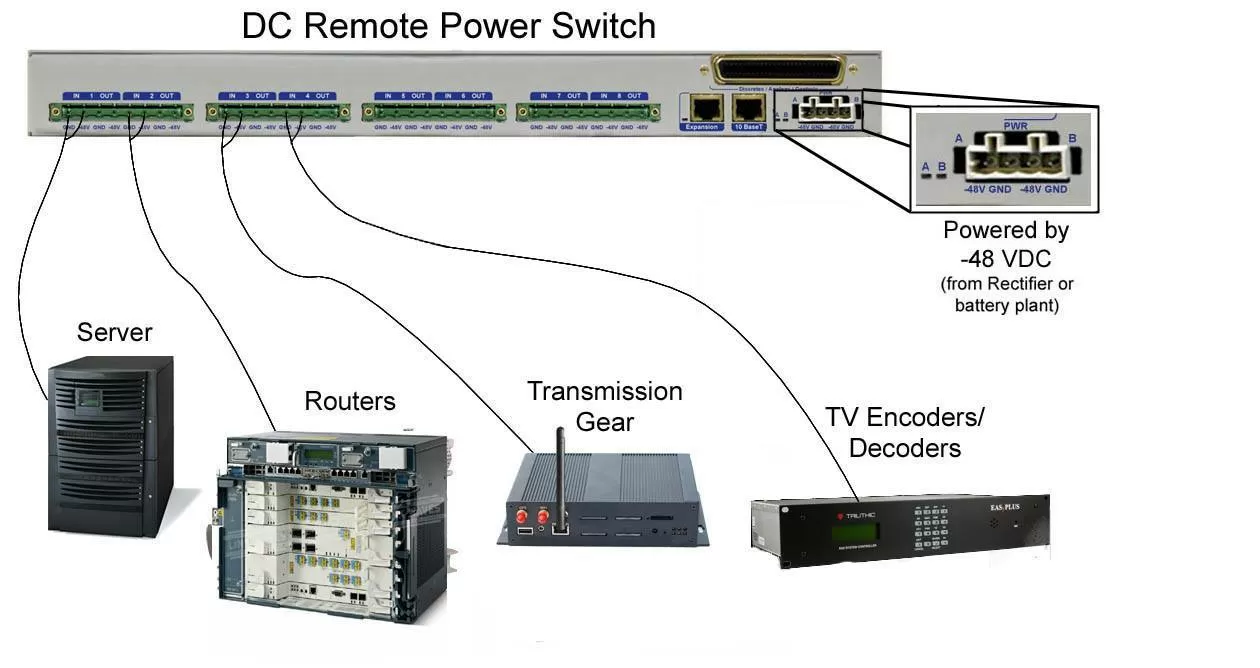
Basic remote power controllers are available from a wide array of manufacturers, but the DC Remote Power Switch includes more functionality than the rest. It can have both a power controller and an RTU in only one box. With the RTU build option, you'll get 16 discrete alarm points, 2 analog alarm points, 2 control relays, and 1 internal temperature sensor - all in the same chassis.
Another aspect that makes this power controller special and different from so many others is its SNMP compatibility. The Remote Power Switch can send SNMP traps and/or receive email alerts. Also, you can choose up to 8 notification devices, being any combination of SNMP managers and email addresses.
The DC Remote Power Controller can be used in many different settings. If you'd like to know more about this device and how it can help your network, just reach out to us and ask for a free web demo.

Morgana Siggins
Morgana Siggins is a marketing writer, content creator, and documentation specialist at DPS Telecom. She has created over 200 blog articles and videos sharing her years of experience in the remote monitoring industry.