Check out our White Paper Series!
A complete library of helpful advice and survival guides for every aspect of system monitoring and control.
1-800-693-0351
Have a specific question? Ask our team of expert engineers and get a specific answer!
Sign up for the next DPS Factory Training!

Whether you're new to our equipment or you've used it for years, DPS factory training is the best way to get more from your monitoring.
Reserve Your Seat TodayFiber is everywhere. However, many organizations are not completely adapted to properly work with it.
We've been a network monitoring solutions manufacturer for more than 30 years, and we've had many companies reaching out to us after a major outage caused by the lack of fiber fault monitoring. That's why we make sure to alert you that to avoid outages you need to have an early detection plan. With advanced notification of broken links and faults, you'll instantly get the upper hand in preventing outages.
How does fiber fault detection technology work? I'll explain it to you in this article.
You'll learn how to efficiently monitor fiber optic networks, and we'll also walk through the necessary components of a complete fiber fault monitoring system and the benefits of fiber fault management. This way you'll have the knowledge to make the right decisions for your network.

Fiber optic cable provides you with access to your network, which connects you to all of your customers, resources, and systems. This connection provides your customers and/or users with the services you have promised.
It is vital to know all potential problems within your fiber optic network, as your business depends on its productivity.
The data center segments of networks can be considered the "edge" of the overall access network. Almost all optical network access points fall within the range of 40km or below. There are tons of connections, splices, patch-panels, and miles of optical fiber in this area which make it particularly vulnerable to breaks and other potential problems. These potential problems are magnified by a large number of possible failure points in this segment.
Optical Time Domain Reflectometry (OTDR) is the function that monitors your fiber optic cables in order to detect cuts, breaks, or other faults. There are solutions out there that can help monitor for these issues, but they don't have a fast, efficient, and physical layer approach that allows for instantaneous identification, localization, and reporting (via SNMP).
Centralized OTDR systems:
Are sophisticated, costly systems that monitor small numbers of optical fibers at any point of time.
In effect, consume these fibers and render them unavailable for revenue-generating functions (transferring data) as their only function is for monitoring.
Are an extremely inefficient method in the high link density environment at the "edge" of the access network. In the "edge" of network, link distances are relatively short (less than 40km). Requirements of an OTDR to operate in this segment are modest.
Introducing fewer, higher performance (much more expensive) systems might not be as efficient as distributing a large number of performance monitors and their OTDRs throughout the network.
To fully monitor and report the status of a fiber optic network, distributed performance monitors need to be placed everywhere. You can achieve close to 100% detection when all links incorporate performance monitoring.
Fault detection within fiber cables is based upon reflected light signals from a fault's origin. Fiber faults and intermittent connections produce optical reflections of varying intensities. The reflection intensity of a fiber break has a known statistical distribution.
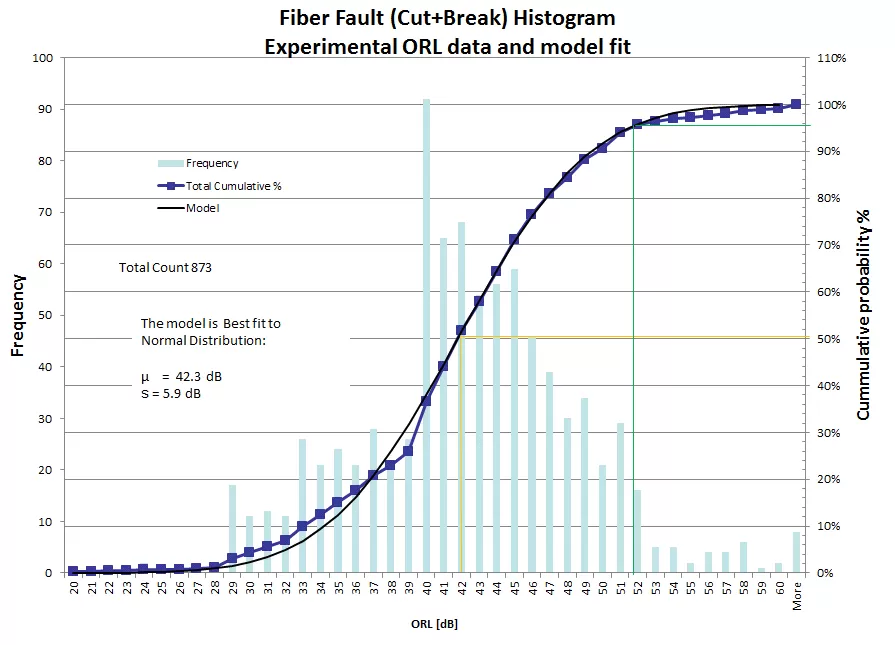
As you can see in the graph above, to achieve a 95% detection probability, the detection circuit needs to be better than 51dB. Using this graph and the known normal distribution, it is possible to predict outcomes.
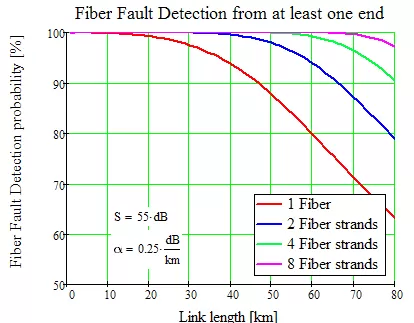
The ability to monitor multiple fibers within the same cable trunk can increase the probability of detecting faults as each fiber breaks differently. Optical fiber links may be monitored from one or both sides when a ring network topology is in use. When monitoring both ends, the probability of detection which may be achieved for a fiber break is much improved and is shown in the graph above.
The logical place to put performance monitoring is in the optical transceivers for fiber cables, which by necessity MUST reside at both ends of every optical link within the access network. With performance monitoring distributed throughout the entire network, the probability of the detection, localization, and reporting (via SNMP) of fiber faults is greatly increased.
Transceivers must be of the single fiber, single wavelength (SFSW) category in order to do their jobs as an OTDR. This means that it will both transmit and receive at the same wavelength, which in effect doubles the fiber optic plant capacity.
When there is a disruption of the data link detected, the transceiver will turn into "Micro-OTDR" mode and begin emitting optical power pulses in order to detect reflections generated by physical faults in a fiber link.
These pulses are greater than +13 dBm, and the transceiver must detect reflections at least down to -42 dBm optical power in order to achieve a dynamic range of 55 dB.
A very high pulsed laser diode driver and a specialized threshold receiver that detects the reflections with higher sensitivity than the data receiver are key aspects of a transceiver with OTDR functionality. They combine to make the dynamic 55dB range discussed earlier a possibility.
Should use standard SNMP for easy configuration/monitoring. This means it can be easily integrated into existing switch/router equipment with minimal software/firmware upgrades.
The solution should be fast, efficient, and at the physical layer.
Backward and forward compatibility is necessary for new and legacy systems.
The solution should not require specialty equipment. Works with fiber-capable RTUs and SNMP managers.
Must have the ability to instantaneously identify, locate, and report problems (via SNMP) within your fiber optic network.
You rely fully on your fiber optic network to deliver the products and services that your business needs to succeed. There is a way to monitor its status and fix problems more quickly and efficiently than ever. There are a few key advantages that make it imperative to do so.
Minimized SLA payments
As a business, you agree to a certain level of service when contracting with customers. When those services aren't up to par, you must compensate your customers financially. The ability to detect and correct faults quickly within your fiber optic network translates into fewer disruptions in service for your customers. This means that you can meet your service level agreement and avoid compensating for disruptions.
Increased SLA payments from customers
As you monitor and quickly repair problems within your fiber optic network, service levels will reach their highest potential. You will have the ability to meet your contracted SLAs and receive payment from customers.
Attract new customers
Your clients want to have a great experience when using your service. This is true for any industry and any company. Very few disruptions in your network allow you to do business as efficiently and professionally as possible. Customers will appreciate the higher standard you will be able to achieve when your network is running properly more of the time and your processes go uninterrupted.
Retain existing customers
When services go uninterrupted more of the time, your customers will have no need to look for other providers.
Pinpoint location of faults
Micro-OTDR/SFPs have the ability to ascertain a more precise location of faults that may occur. No more guessing is involved when trying to repair, saving you time and money.
Reduce operational costs
The fast, efficient, physical layer monitoring that is achieved when utilizing Micro-OTDRs means that the right team will be dispatched to the right area the first time when there is a problem within your fiber optic network. You will reduce the time it takes to repair the problem, and you will avoid excess labor costs.
We all know that finding the right vendor for products can be difficult. With so many options out there, it is important to focus on specifics, value, and support. You now know exactly what type of performance monitoring solution you should be looking for. What other aspects should you take into consideration?
Choose a proven industry-leading company that backs its products up with a guarantee. This way, you are not locked into a product that might end up being the wrong choice. A company that is confident in their products will offer a money-back guarantee if you are not satisfied.
Exceptional support is a necessary characteristic of the company you choose to purchase your fiber optic performance monitoring solution from. Tech support should be available 24/7 in case any problems are encountered with your equipment. After all, you are depending on it to keep your network running.
The recommended Micro-OTDR/SFP solution requires other monitoring system components (such as fiber-capable RTUs or SNMP managers) that you may or may not already have in place. A company that has formed partnerships with other proven industry leaders will benefit you greatly. Having access to a trusted company's products will help you acquire all the system components confidently and quickly.
Choose a company that has exactly what you need. Do not settle for products that don't have your specifications; find a company that will do whatever it can to fulfill your needs as its customer. Your network is too vital to settle for less.
How does this fiber fault detection technology work? Whenever the data link breaks, a pulse of light is instantly shot through the optical fibers and is reflected back. The timing on the returned pulse pinpoints the location of the fault.
Traditionally, many fault detectors had poor performance and operational problems. First, they would occupy an entire optical shelf, which is inefficient. Secondly, they were sensitive to the noise caused by the return reflections.
However, a new "reflection immune" design overcomes these previous limitations by using special firmware to make these single fiber, single wavelength (SFSW) SFP Transceivers immune to reflections. This transceiver is also capable of CWDM data transport in normal use. You won't have to dedicate an entire fiber for monitoring, nor will you sacrifice a CWDM channel, so you'll have more optical fibers for revenue generation.
The bottom line is: you're instantly notified of faults in your fiber transports. This saves you operational expense dollars and helps you quickly get back online during outages (such as disaster-recovery situations).
Detecting a fault is just the first step in the equation. Ideally, whenever the data link is broken, you should quickly be notified (via email, SMS text message, phone call, SNMP, etc.).
As an experienced network fault monitoring solutions provider, we can provide you with a perfect-fit device to monitor your fiber optic networks. Our T/Mon master station provides thorough coverage over all Micro-OTDR fault detectors. It not only has scalable capacity, but also can monitor other network elements - helping you maximize your ROI.
Without the right visibility, a fault could go unnoticed for far too long. We can provide you the means to keep you apprised of all faults and breaks in your fiber transports. Call us and start your project today.

Morgana Siggins
Morgana Siggins is a marketing writer, content creator, and documentation specialist at DPS Telecom. She has created over 200 blog articles and videos sharing her years of experience in the remote monitoring industry.